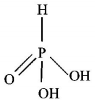
181.
Consider the following sequence of conversion.
$$X, Y$$ and $$Z$$ can be described as
| X | Y | Z | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (a) | Colourless | Brown, paramagnetic | Colourless, diamagnetic |
| (b) | Brown | Colourless, diamagnetic | Brown, paramagnetic |
| (c) | Colourless | Colourless, paramagnetic | Brown, diamagnetic |
| (d) | Brown | Brown, paramagnetic | Brown, diamagnetic |
A
(a)
B
(b)
C
(c)
D
(d)
Answer :
(a)
182. Which of the following is similar to graphite ?
A
$$B$$
B
$$BN$$
C
$${B_2}{H_6}$$
D
$${B_4}C$$
Answer :
$$BN$$
183. Polyphosphates are used as water softening agents because they
A
form soluble complexes with anionic species
B
precipitate anionic species
C
form soluble complexes with cationic species
D
precipitate cationic species
Answer :
form soluble complexes with cationic species
184. Which of the following statements is not correct about $$Xe{F_2}?$$
A
It can be obtained by direct reaction between $${F_2}$$ and $$Xe$$ at high pressure.
B
$$Xe{F_2}$$ undergoes alkaline hydrolysis to give $${O_2}$$ and $$Xe.$$
C
$$Xe{F_2}$$ is a powerful reducing agent.
D
$$Xe{F_2}$$ contains two bond pairs and three lone pairs.
Answer :
$$Xe{F_2}$$ is a powerful reducing agent.
185. The reaction of $${P_4}$$ with $$X$$ leads selectively to $${P_4}{O_6}$$ . The $$X$$ is
A
$$\,{\text{Dry}}\,{O_2}$$
B
A mixture of $${O_2}\,{\text{and}}\,{N_2}$$
C
Moist $${O_2}$$
D
$${O_2}$$ in the presence of aqueous $$NaOH$$
Answer :
A mixture of $${O_2}\,{\text{and}}\,{N_2}$$
186. Which one of the following oxides is neutral?
A
$$CO$$
B
$$Sn{O_2}$$
C
$$ZnO$$
D
$$Si{O_2}$$
Answer :
$$CO$$
187. Noble gases do not react with other elements because
A
they are monoatomic
B
they are found in abundance
C
the size of their atoms is very small
D
they are completely paired up and have stable electron shells
Answer :
they are completely paired up and have stable electron shells
188. $${H_2}S{O_4}$$ cannot be used to prepare $$\,HBr$$ from $$NaBr$$ as it :
A
reacts slowly with $$NaBr$$
B
oxidises $$\,HBr$$
C
reduces $$\,HBr$$
D
disproportionates $$\,HBr$$
Answer :
oxidises $$\,HBr$$
189. $${H_3}P{O_3}\,{\text{and}}\,{H_3}P{O_4}$$ the correct choice is:
A
$${H_3}P{O_3}$$ is dibasic and reducing
B
$${H_3}P{O_3}$$ is dibasic and non-reducing
C
$${H_3}P{O_4}$$ is tribasic and reducing
D
$${H_3}P{O_3}$$ is tribasic and non-reducing
Answer :
$${H_3}P{O_3}$$ is dibasic and reducing
190. The temporary hardness of water due to calcium carbonate can be removed by adding —
A
$$CaC{O_3}$$
B
$$Ca{\left( {OH} \right)_2}\,$$
C
$$CaC{l_2}$$
D
$$\,HCl$$
Answer :
$$Ca{\left( {OH} \right)_2}\,$$