211. Inductive effect involves
A
displacement of $$\sigma $$ - electrons resulting in polarisation
B
displacement of $$\pi $$ - electrons resulting in polarisation
C
delocalisation of $$\sigma $$ - electrons
D
delocalisation of $$\pi $$ - electrons
Answer :
displacement of $$\sigma $$ - electrons resulting in polarisation
212.
The chirality of the compound
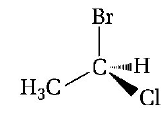 is
is
A
$$R$$
B
$$S$$
C
$$Z$$
D
$$E$$
Answer :
$$R$$
213. If on adding $$FeC{l_3}$$ solution to acidified Lassaigne solution, a blood red colouration is produced, it indicates the presence of
A
$$S$$
B
$$N$$
C
$$N\,{\text{and}}\,S$$
D
$$S\,{\text{and}}\,Cl$$
Answer :
$$N\,{\text{and}}\,S$$
214. During hearing of a court case, the judge suspected that some changes in the documents had been carried out. He asked the forensic department to check the ink used at two different places. According to you which technique can give the best results?
A
Column chromatography
B
Solvent extraction
C
Distillation
D
Thin layer chromatography
Answer :
Thin layer chromatography
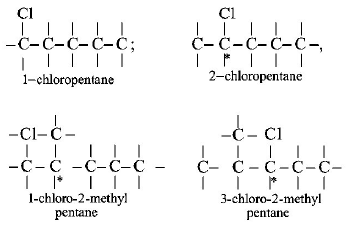
215. Which of the following compounds is not chiral ?
A
1- chloro - 2 - methyl pentane
B
2 - chloropentane
C
1 - chloropentane
D
3 - chloro - 2 - methyl pentane
Answer :
1 - chloropentane
216. Which of the following is the strongest base ?
A
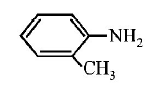

B
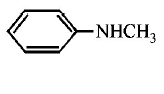

C
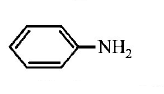

D
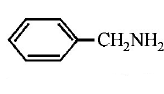

Answer :


217. Hyperconjugation is not possible in
A
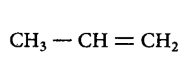
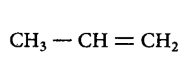
B
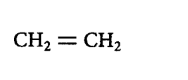
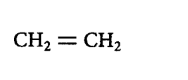
C
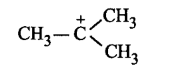

D
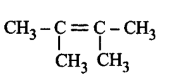
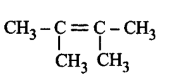
Answer :
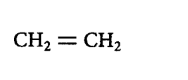
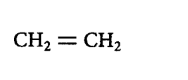
218. Which of the following reactions is an example of nucleophilic substitution reaction?
A
$$RX + KOH \to ROH + KX$$
B
$$2\,RX + 2\,Na \to R - R + 2NaX$$
C
$$RX + {H_2} \to RH + HX$$
D
$$RX + Mg \to RMgX$$
Answer :
$$RX + KOH \to ROH + KX$$
219.
Base strength of
$$\eqalign{
& \left( {\text{i}} \right)\,{H_3}C\mathop C\limits^\Theta \,{H_2} \cr
& \left( {{\text{ii}}} \right)\,{H_2}C = \mathop C\limits^\Theta H \cr
& \left( {{\text{iii}}} \right)H - C \equiv \mathop C\limits^\Theta \cr} $$
is in the order of
A
(ii) > (i) > (iii)
B
(iii) > (ii) > (i)
C
(i) > (iii) > (ii)
D
(i) > (ii) > (iii)
Answer :
(i) > (ii) > (iii)
220.
How many degrees of unsaturation are there in the following compound ?

A
6
B
7
C
10
D
11
Answer :
11