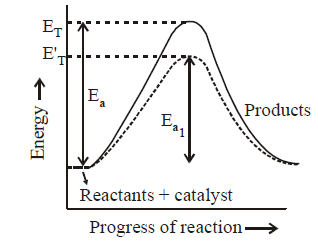
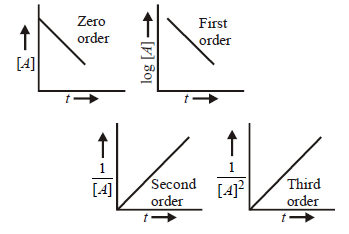
261. $$3A \to B + C$$ It would be a zero order reaction, when
A
the rate of reaction is proportional to square of concentration of $$A$$
B
the rate of reaction remains same at any concentration of $$A$$
C
the rate remains unchanged at any concentration of $$B$$ and $$C$$
D
the rate of reaction doubles if concentration of $$B$$ is increased to double
Answer :
the rate of reaction remains same at any concentration of $$A$$
262. In a chemical reaction $$A$$ is converted into $$B.$$ The rates of reaction, starting with initial concentrations of $$A$$ as $$2 \times {10^{ - 3}}M$$ and $$1 \times {10^{ - 3}}M,$$ are equal to $$2.40 \times {10^{ - 4}}M{s^{ - 1}}$$ and $$0.60 \times {10^{ - 4}}M{s^{ - 1}}$$ respectively. The order of reaction with respect to reactant $$A$$ will be
A
0
B
1.5
C
1
D
2
Answer :
2
263. When a biochemical reaction is carried out in laboratory in the absence of enzyme then rate of reaction obtained is $${10^{ - 6}}$$ times, then activation energy of reaction in the presence of enzyme is
A
$$\frac{6}{{RT}}$$
B
different from $${E_a}$$ obtained in laboratory
C
$$P$$ is required
D
can't say anything
Answer :
different from $${E_a}$$ obtained in laboratory
264. Rate constant $$k = 1.2 \times {10^3}mo{l^{ - 1}}\,L\,{s^{ - 1}}$$ and $${E_a} = 2.0 \times {10^2}kJ\,mo{l^{ - 1}}.$$ When $$T \to \infty :$$
A
$$A = 2.0 \times {10^2}kJ\,mo{l^{ - 1}}$$
B
$$A = 1.2 \times {10^3}\,mo{l^{ - 1}}\,L\,{s^{ - 1}}$$
C
$$A = 1.2 \times {10^3}mol\,{L^{ - 1}}{s^{ - 1}}$$
D
$$A = 2.4 \times {10^3}kJ\,mo{l^{ - 1}}{s^{ - 1}}$$
Answer :
$$A = 1.2 \times {10^3}\,mo{l^{ - 1}}\,L\,{s^{ - 1}}$$
265. The plot of concentration of the reactant Vs time for a reaction is a straight line with a negative slope. The reaction follows a rate equation of
A
zero order
B
first order
C
second order
D
third order
Answer :
zero order
266. A catalyst is a substance which
A
increases the equilibrium concentration of the product
B
changes the equilibrium constant of the reaction
C
shortens the time to reach equilibrium
D
supplies energy to the reaction
Answer :
shortens the time to reach equilibrium
267.
For a reaction, $$2NO + 2{H_2} \to {N_2} + 2{H_2}O,$$ the possible mechanism is
\[\begin{align}
& 2NO\rightleftharpoons {{N}_{2}}{{O}_{2}} \\
& {{N}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}\xrightarrow{\text{slow}}{{N}_{2}}O+{{H}_{2}}O \\
& {{N}_{2}}O+{{H}_{2}}\xrightarrow{\text{fast}}{{N}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}O \\
\end{align}\]
What is the rate law and order of the reaction?
A
$${\text{Rate}} = \left[ {{N_2}{O_2}} \right],{\text{order}} = 1$$
B
$${\text{Rate}} = \left[ {{N_2}{O_2}} \right]\left[ {{H_2}} \right],{\text{order}} = 2$$
C
$${\text{Rate}} = {\left[ {{N_2}{O_2}} \right]^2},{\text{order}} = 2$$
D
$${\text{Rate}} = {\left[ {{N_2}{O_2}} \right]^2}\left[ {{H_2}} \right],{\text{order}} = 3$$
Answer :
$${\text{Rate}} = \left[ {{N_2}{O_2}} \right]\left[ {{H_2}} \right],{\text{order}} = 2$$
268. The radiations from a naturally occurring radioactive substance, as seen after deflection by a magnetic field in one direction, are :
A
definitely alpha rays
B
definitely beta rays
C
both alpha and beta rays
D
either alpha or beta rays
Answer :
either alpha or beta rays
269. The half life of a radioactive element is $$20\,\min .$$ The time interval between the stages of its $$33\% $$ and $$67\% $$ decay is
A
$$40\,\min $$
B
$$20\,\min $$
C
$$30\,\min $$
D
$$25\,\min $$
Answer :
$$20\,\min $$
270. The rate of a reaction increases four-fold when the concentration of reactant is increased 16 times. If the rate of reaction is $$4 \times {10^{ - 6}}mol\,{L^{ - 1}}{s^{ - 1}}$$ when the concentration of the reactant is $$4 \times {10^{ - 4}}\,mol\,{L^{ - 1}}.$$ The rate constant of the reaction will be
A
$$2 \times {10^{ - 4}}\,mo{l^{\frac{1}{2}}}{L^{ - \frac{1}{2}}}{s^{ - 1}}$$
B
$$1 \times {10^{ - 2}}{s^{ - 1}}$$
C
$$2 \times {10^{ - 4}}mo{l^{ - \frac{1}{2}}}{L^{\frac{1}{2}}}{s^{ - 1}}$$
D
\[25\,mo{{l}^{-1}}L\,{{\min }^{-1}}\]
Answer :
$$2 \times {10^{ - 4}}\,mo{l^{\frac{1}{2}}}{L^{ - \frac{1}{2}}}{s^{ - 1}}$$