61.
Water falls from a height of $$60\,m$$ at the rate of $$15\,kg/s$$ to operate a turbine. The losses due to frictional force are $$10\% $$ of energy. How much power is generated by the turbine?
$$\left( {g = 10\,m/{s^2}} \right)$$
A
$$8.1\,kW$$
B
$$10.2\,kW$$
C
$$12.3\,kW$$
D
$$7.0\,kW$$
Answer :
$$8.1\,kW$$
62. A body of mass $$10\,kg$$ moves with a velocity $$v$$ of $$2\,m/s$$ along a circular path of radius $$8\,m.$$ The power produced by the body will be
A
$$10\,J/s$$
B
$$98\,J/s$$
C
$$49\,J/s$$
D
zero
Answer :
zero
63.
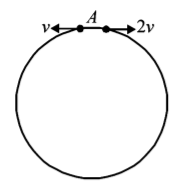
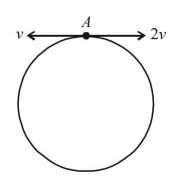
Two small particles of equal masses start moving in opposite directions from a point $$A$$ in a horizontal circular orbit. Their tangential velocities are $$v$$ and $$2v,$$ respectively, as shown in the figure. Between collisions, the particles move with constant speeds. After making how many elastic collisions, other than that at $$A,$$ these two particles will again reach the point $$A$$ ?
A
4
B
3
C
2
D
1
Answer :
2
64. A particle of mass $$m$$ is moving in a circular path of constant radius $$r$$ such that its centripetal acceleration $${a_c}$$ is varying with time $$t$$ as $${a_c} = {k^2}r{t^2}$$ where $$k$$ is a constant. The power delivered to the particles by the force acting on it is
A
$$2\pi m{k^2}{r^2}t$$
B
$$m{k^2}{r^2}t$$
C
$$\frac{{\left( {m{k^4}{r^2}{t^5}} \right)}}{3}$$
D
zero
Answer :
$$m{k^2}{r^2}t$$
65. The coefficient of restitution $$e$$ for a perfectly elastic collision is
A
$$1$$
B
zero
C
infinite
D
$$- 1$$
Answer :
$$1$$
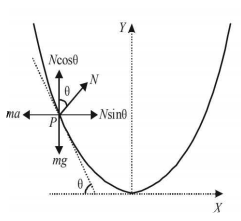
66. A piece of wire is bent in the shape of a parabola $$y = k{x^2}$$ ($$y$$-axis vertical) with a bead of mass $$m$$ on it. The bead can slide on the wire without friction. It stays at the lowest point of the parabola when the wire is at rest. The wire is now accelerated parallel to the $$x$$-axis with a constant acceleration $$a.$$ The distance of the new equilibrium position of the bead, where the bead can stay at rest with respect to the wire, from the $$y$$-axis is-
A
$$\frac{a}{{gk}}$$
B
$$\frac{a}{{2gk}}$$
C
$$\frac{{2a}}{{gk}}$$
D
$$\frac{a}{{4gk}}$$
Answer :
$$\frac{a}{{2gk}}$$
67. A stone is thrown at an angle of $${45^ \circ }$$ to the horizontal with kinetic energy $$K.$$ The kinetic energy at the highest point is
A
$$\frac{K}{2}$$
B
$$\frac{K}{{\sqrt 2 }}$$
C
$$K$$
D
zero
Answer :
$$\frac{K}{2}$$
68. A particle is acted by a force $$F= kx,$$ where $$k$$ is a $$+ve$$ constant. Its potential energy at $$x = 0$$ is zero. Which curve correctly represents the variation of potential energy of the block with respect to $$x$$
A
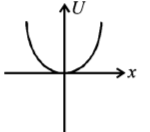

B
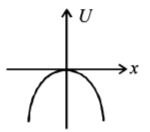

C
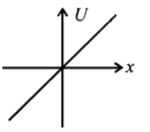

D
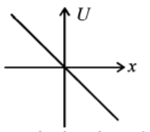

Answer :


69. Two masses of $$1 \,gm$$ and $$4 \,gm$$ are moving with equal kinetic energies. The ratio of the magnitudes of their linear momenta is-
A
$$4:1$$
B
$$\sqrt 2 :1$$
C
$$1:2$$
D
$$1:16$$
Answer :
$$1:2$$
70. Two identical balls $$A$$ and $$B$$ moving with velocities $$+ 0.5\,m/s$$ and $$- 0.3\,m/s$$ respectively, collide head on elastically. The velocity of the balls $$A$$ and $$B$$ after collision will be respectively
A
$$ + 0.5\,m/s\,{\text{and}}\, + 0.3\,m/s$$
B
$$ - 0.3\,m/s\,{\text{and}}\, + 0.5\,m/s$$
C
$$ + 0.3\,m/s\,{\text{and}}\,0.5\,m/s$$
D
$$ - 0.5\,m/s\,{\text{and}}\, + 0.3\,m/s$$
Answer :
$$ - 0.3\,m/s\,{\text{and}}\, + 0.5\,m/s$$
.PNG)