21. If $$x + \lambda y - 2$$ and $$x - \mu y + 1$$ are factors of the expression $$6{x^2} - xy - {y^2} - 6x + 8y - 12$$ then
A
$$\lambda = \frac{1}{3},\mu = \frac{1}{2}$$
B
$$\lambda = 2,\mu = 3$$
C
$$\lambda = \frac{1}{3},\mu = - \frac{1}{2}$$
D
None of these
Answer :
$$\lambda = \frac{1}{3},\mu = \frac{1}{2}$$
22. If the equations $$a{x^2} + bx + c = 0$$ and $$c{x^2} + bx + a = 0,a \ne c$$ have a negative common root then the value of $$a - b + c$$ is
A
0
B
2
C
1
D
None of these
Answer :
0
23. If $$a, b, c$$ are non-zero, unequal rational numbers then the roots of the equation $$ab{c^2}{x^2} + \left( {3{a^2} + {b^2}} \right)cx - 6{a^2} - ab + 2{b^2} = 0$$ are
A
rational
B
imaginary
C
irrational
D
none of these
Answer :
rational
24. If $$X$$ denotes the set of real numbers $$p$$ for which the equation $${x^2} = p\left( {x + p} \right)$$ has its roots greater than $$p$$ then $$X$$ is equal to
A
$$\left( { - 2, - \frac{1}{2}} \right)$$
B
$$\left( { - \frac{1}{2},\frac{1}{4}} \right)$$
C
null set $$\phi $$
D
$$\left( { - \infty ,0} \right)$$
Answer :
null set $$\phi $$
25.
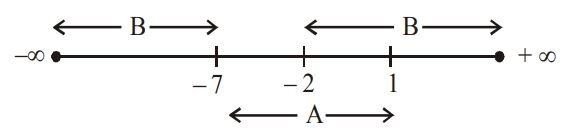
If $$A = \left\{ {x \in IR:{x^2} + 6x - 7 < 0} \right\}$$ and $$B = \left\{ {x \in IR:{x^2} + 9x + 14 > 0} \right\},$$ then which of the
following is/ are correct ?
$$\eqalign{
& 1.\left( {A \cap B} \right) = \left( { - 2,1} \right) \cr
& 2.\left( {\frac{A}{B}} \right) = \left( { - 7, - 2} \right) \cr} $$
Select the correct answer using the code given below :
A
1 only
B
2 only
C
Both 1 and 2
D
Neither 1 nor 2
Answer :
Both 1 and 2
26. The equation $$x + 2y + 2z = 1{\text{ and }}2x + 4y + 4z = 9{\text{ have}}$$
A
Only one solution
B
Only two solutions
C
Infinite number of solutions
D
None of these
Answer :
None of these
27. The equation $$2{\sin ^2}\frac{x}{2} \cdot {\cos ^2}x = x + \frac{1}{x},0 < x \leqslant \frac{\pi }{2}$$ has
A
one real solution
B
no real solution
C
infinitely many real solutions
D
none of these
Answer :
no real solution
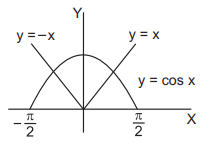
28. The number of solutions of the equation $$\left| x \right| = \cos x$$ is
A
one
B
two
C
three
D
zero
Answer :
two
29. The number of real solutions of the equation $${x^2} - 3\left| x \right| + 2 = 0\,\,{\text{is}}$$
A
3
B
2
C
4
D
1
Answer :
4
30. Difference between the corresponding roots of $${x^2} + ax + b = 0\,\,{\text{and }}\,{x^2} + bx + a = 0$$ is same and $$a \ne b,$$ then
A
$$a + b + 4 = 0$$
B
$$a + b - 4 = 0$$
C
$$a - b - 4 = 0$$
D
$$a - b + 4 = 0$$
Answer :
$$a + b + 4 = 0$$