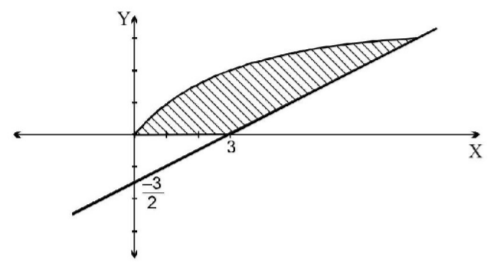
121. The area (in square units) bounded by the curves $$y = \sqrt x ,\,2y - x + 3 = 0,$$ $$x$$-axis, and lying in the first quadrant is:
A
$$9$$
B
$$36$$
C
$$18$$
D
$$\frac{{27}}{4}$$
Answer :
$$9$$
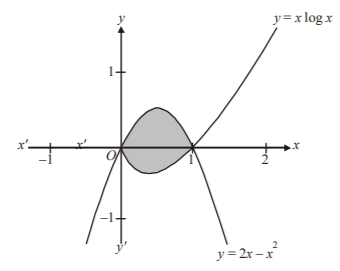
122. The area of the region enclosed by the curves $$y = x\,{\log _e}x$$ and $$y = 2x - 2{x^2}$$ is :
A
$$\frac{5}{{12}}$$
B
$$\frac{7}{{12}}$$
C
$$1$$
D
$$\frac{4}{7}$$
Answer :
$$\frac{7}{{12}}$$
123. $$\int_1^3 {\left| {\left( {2 - x} \right){{\log }_e}x} \right|dx} $$ is equal to :
A
$$\frac{3}{2}{\log _e}3 + \frac{1}{2}$$
B
$${\log _e}\frac{{16}}{{3\sqrt 2 }} - \frac{1}{2}$$
C
$$ - \frac{3}{2}{\log _e}3 - \frac{1}{2}$$
D
none of these
Answer :
$${\log _e}\frac{{16}}{{3\sqrt 2 }} - \frac{1}{2}$$
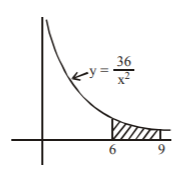
124. The area enclosed by the curve $${x^2}y = 36,$$ the $$x$$-axis and the lines $$x = 6$$ and $$x = 9$$ is :
A
6
B
1
C
4
D
2
Answer :
2
125. The value of $$a\left( {a > 0} \right)$$ for which the area bounded by the curves $$y = \frac{x}{6} + \frac{1}{{{x^2}}},\,y = 0,\,x = a$$ and $$x = 2a$$ has the least value is :
A
$$2$$
B
$$\sqrt 2 $$
C
$${2^{\frac{1}{3}}}$$
D
$$1$$
Answer :
$$1$$
126. The value of $$\int_0^1 {\left( {1 + {e^{ - {x^2}}}} \right)dx} $$ is :
A
$$-1$$
B
2
C
$$1 + {e^{ - 1}}$$
D
none of these
Answer :
none of these
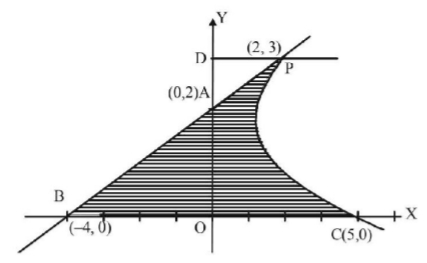
127. The area of the region bounded by the parabola $${\left( {y - 2} \right)^2} = x - 1,$$ the tangent of the parabola at the point (2, 3) and the $$x$$-axis is:
A
$$6$$
B
$$9$$
C
$$12$$
D
$$3$$
Answer :
$$9$$
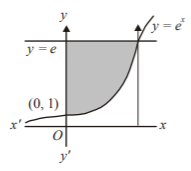
128. Which of the following is not the area of the region bounded by $$y = {e^x}$$ and $$x = 0$$ and $$y = e\,?$$
A
$$e - 1$$
B
$$\int\limits_1^e {\ln \left( {e + 1 - y} \right)dy} $$
C
$$e - \int\limits_0^1 {{e^x}dx} $$
D
$$\int\limits_1^e {\ln \,y\,dy} $$
Answer :
$$e - \int\limits_0^1 {{e^x}dx} $$
129. Let $$f\left( x \right)$$ be a non-negative continuous function such that the area bounded by the curve $$y = f\left( x \right),$$ $$x$$-axis and the ordinates $$x = \frac{\pi }{4}$$ and $$x = \beta > \frac{\pi }{4}$$ is $$\left( {\beta \,\sin \,\beta + \frac{\pi }{4}\cos \,\beta + \sqrt 2 \beta } \right).$$ Then $$f\left( {\frac{\pi }{2}} \right)$$ is-
A
$$\left( {\frac{\pi }{4} + \sqrt 2 - 1} \right)$$
B
$$\left( {\frac{\pi }{4} - \sqrt 2 + 1} \right)$$
C
$$\left( {1 - \frac{\pi }{4} - \sqrt 2 } \right)$$
D
$$\left( {1 - \frac{\pi }{4} + \sqrt 2 } \right)$$
Answer :
$$\left( {1 - \frac{\pi }{4} + \sqrt 2 } \right)$$
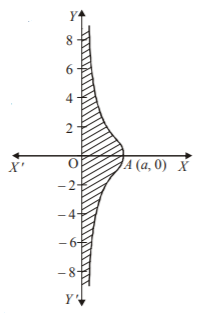
130. Area bounded by the curve $$x{y^2} = {a^2}\left( {a - x} \right)$$ and $$y$$-axis is :
A
$$\frac{{\pi {a^2}}}{2}{\text{ sq}}{\text{. units}}$$
B
$$\pi {a^2}{\text{ sq}}{\text{. units}}$$
C
$$3\pi {a^2}{\text{ sq}}{\text{. units}}$$
D
None of these
Answer :
$$\pi {a^2}{\text{ sq}}{\text{. units}}$$