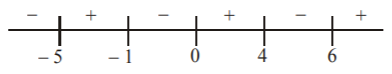111. The domain of the function $$f\left( x \right) = {\log _{3 + x}}\left( {{x^2} - 1} \right)$$ is :
A
$$\left( { - 3,\, - 1} \right) \cup \left( {1,\,\infty } \right)$$
B
$$\left[ { - 3,\, - 1} \right) \cup \left[ {1,\,\infty } \right)$$
C
$$\left( { - 3,\, - 2} \right) \cup \left( { - 2,\, - 1} \right) \cup \left( {1,\,\infty } \right)$$
D
$$\left[ { - 3,\, - 2} \right) \cup \left( { - 2,\, - 1} \right) \cup \left[ {1,\,\infty } \right)$$
Answer :
$$\left( { - 3,\, - 2} \right) \cup \left( { - 2,\, - 1} \right) \cup \left( {1,\,\infty } \right)$$
112. The domain of the function $$f\left( x \right) = \sqrt {x - \sqrt {1 - {x^2}} } $$ is :
A
$$\left[ { - 1,\, - \frac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right] \cup \left[ {\frac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }},\,1} \right]$$
B
$$\left[ { - 1,\,1} \right]$$
C
$$\left( { - \infty ,\, - \frac{1}{2}} \right] \cup \left[ {\frac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }},\, + \infty } \right)$$
D
$$\left[ {\frac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }},\,1} \right]$$
Answer :
$$\left[ {\frac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }},\,1} \right]$$
113. If a function $$F$$ is such that $$F\left( 0 \right) = 2,\,F\left( 1 \right) = 3,\,F\left( {x + 2} \right) = 2F\left( x \right) - F\left( {x + 1} \right)$$ for $$x \geqslant 0,$$ then $$F\left( 5 \right)$$ is equal to :
A
$$ - 7$$
B
$$ - 3$$
C
$$17$$
D
$$13$$
Answer :
$$13$$
114. $$f\left( x \right) = x + \sqrt {{x^2}} $$ is a function from $$R \to R.$$ Then $$f\left( x \right)$$ is :
A
injective
B
surjective
C
bijective
D
none of these
Answer :
none of these
115. If $$f:R \to R$$ satisfies $$f\left( {x + y} \right) = f\left( x \right) + f\left( y \right),$$ for all $$x,y \in R$$ and $$f\left( 1 \right) = 7,$$ then $$\sum\limits_{r = 1}^n f \left( r \right)$$ is
A
$$\frac{{7n\left( {n + 1} \right)}}{2}$$
B
$$\frac{{7n}}{2}$$
C
$$\frac{{7\left( {n + 1} \right)}}{2}$$
D
$$7n + \left( {n + 1} \right).$$
Answer :
$$\frac{{7n\left( {n + 1} \right)}}{2}$$
116. If $$f\left( x \right) = \frac{1}{{\sqrt {\left( {x + 1} \right)\left( {{e^x} - 1} \right)\left( {x - 4} \right)\left( {x + 5} \right)\left( {x - 6} \right)} }}$$ then the domain of $$f\left( x \right)$$ is :
A
$$\left( { - \infty ,\, - 5} \right) \cup \left( { - 1,\,4} \right) \cup \left( {6,\,\infty } \right)$$
B
$$\left( { - \infty ,\, - 5} \right) \cup \left( { - 1,\,0} \right) \cup \left( {0,\,4} \right) \cup \left( {6,\,\infty } \right)$$
C
$$\left( { - 5,\, - 1} \right) \cup \left( {0,\,4} \right) \cup \left( {6,\,\infty } \right)$$
D
none of these
Answer :
$$\left( { - 5,\, - 1} \right) \cup \left( {0,\,4} \right) \cup \left( {6,\,\infty } \right)$$
117. Let $$f\left( x \right) = x,\,g\left( x \right) = \frac{1}{x}$$ and $$h\left( x \right) = f\left( x \right)g\left( x \right).$$ Then, $$h\left( x \right) = 1$$ if and only if :
A
$$x$$ is a real number
B
$$x$$ is a rational number
C
$$x$$ is an irrational number
D
$$x$$ is a non-zero real number
Answer :
$$x$$ is a non-zero real number
118. Let $$f,g$$ and $$h$$ be real-valued functions defined on the interval $$\left[ {0,1} \right]$$ by $$f\left( x \right) = {e^{{x^2}}} + {e^{ - x^2}},g\left( x \right) = x{e^{{x^2}}} + {e^{ - {x^2}}}$$ and $$h\left( x \right) = {x^2}{e^{{x^2}}} + {e^{ - {x^2}}}.$$ If $$a,b$$ and $$c$$ denote, respectively, the absolute maximum of $$f,g$$ and $$h$$ on $$\left[ {0,1} \right],$$ then
A
$$a = b\,{\text{and}}\,c \ne b$$
B
$$a = c\,{\text{and}}\,a \ne b$$
C
$$a \ne b\,{\text{and}}\,c \ne b$$
D
$$a = b\,{\text{ = }}\,c$$
Answer :
$$a = b\,{\text{ = }}\,c$$
119. The function $$f\left( x \right) = x - \left[ x \right] + \cos \,x,$$ where $$\left[ x \right] = $$ the greatest integer less than or equal to $$x,$$ is a :
A
periodic function of indeterminate period
B
periodic function of period $${2\pi }$$
C
non-periodic function
D
periodic function of period 1
Answer :
non-periodic function
120. The largest interval lying in $$\left( {\frac{{ - \pi }}{2},\frac{\pi }{2}} \right)$$ for which the function, $$f\left( x \right) = {4^{ - {x^2}}} + {\cos ^{ - 1}}\left( {\frac{x}{2} - 1} \right) + \log \left( {\cos x} \right),$$ is defined, is
A
$$\left[ { - \frac{\pi }{4},\frac{\pi }{2}} \right)$$
B
$$\left[ {0,\frac{\pi }{2}} \right)$$
C
$$\left[ {0,\pi } \right]$$
D
$$\left( { - \frac{\pi }{2},\frac{\pi }{2}} \right)$$
Answer :
$$\left[ {0,\frac{\pi }{2}} \right)$$